Experiencing short luteal phases? Prometrium, a progesterone supplement, may help. This medication addresses potential deficiencies, aiming to support a healthy pregnancy. Its efficacy is linked to improving endometrial receptivity, a key factor in successful implantation.
Clinical studies show Prometrium’s positive impact on pregnancy rates in women with diagnosed luteal phase defects. However, individual responses vary, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment plans guided by your healthcare provider. They will assess your specific situation and determine the appropriate dosage and treatment duration.
Remember, Prometrium isn’t a guaranteed solution for infertility. It’s a targeted therapy focusing on one potential aspect of fertility challenges. Your doctor will consider other factors and possibly recommend additional investigations or treatments alongside Prometrium, creating a holistic approach to your care. Open communication with your physician is crucial for effective management.
Potential side effects include mood changes, breast tenderness, and headaches. These are not experienced by all patients. Discuss any concerns or unusual symptoms promptly with your doctor. Consistent monitoring and open dialogue ensure you receive optimal support and address any issues swiftly.
- Prometrium for Luteal Phase Defect
- Understanding Luteal Phase Defect and its Symptoms
- Recognizing the Signs
- Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
- How Prometrium Works to Correct Luteal Phase Deficiency
- Mimicking the Natural Process
- Specific Actions and Results
- Important Note
- Dosage and Administration of Prometrium for LPD
- Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Prometrium
- Serious Side Effects
- Prometrium vs. Other Treatments for Luteal Phase Defect
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Alternative Therapies
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prometrium and LPD
- Prometrium Side Effects: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Concerns About Dosage or Treatment Plan
Prometrium for Luteal Phase Defect
Prometrium, containing micronized progesterone, effectively treats luteal phase defect (LPD) by supplementing the body’s natural progesterone production. This helps to support the uterine lining, increasing the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
Dosage typically ranges from 100mg to 200mg daily, starting around day 12 of the menstrual cycle and continuing until approximately 10 weeks of gestation, or as directed by your physician. Your doctor will tailor the dosage to your individual needs, considering your medical history and response to treatment. Always follow their instructions precisely.
Potential side effects include: breast tenderness, bloating, mood changes, and fatigue. These are generally mild and transient. However, you should immediately contact your healthcare provider if you experience severe or persistent side effects.
Prometrium’s efficacy for LPD is supported by various studies, but the results are not uniform across all studies. Individual responses vary.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Breast tenderness | Common | Mild to moderate |
| Bloating | Common | Mild to moderate |
| Mood changes | Moderate | Mild to moderate |
| Fatigue | Moderate | Mild |
Prometrium is a prescription medication. A thorough discussion with your doctor is crucial before starting treatment. They will assess your specific situation, conduct necessary tests, and determine if Prometrium is the appropriate treatment for you. Regular monitoring throughout treatment is also advised.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult your physician for personalized guidance and treatment.
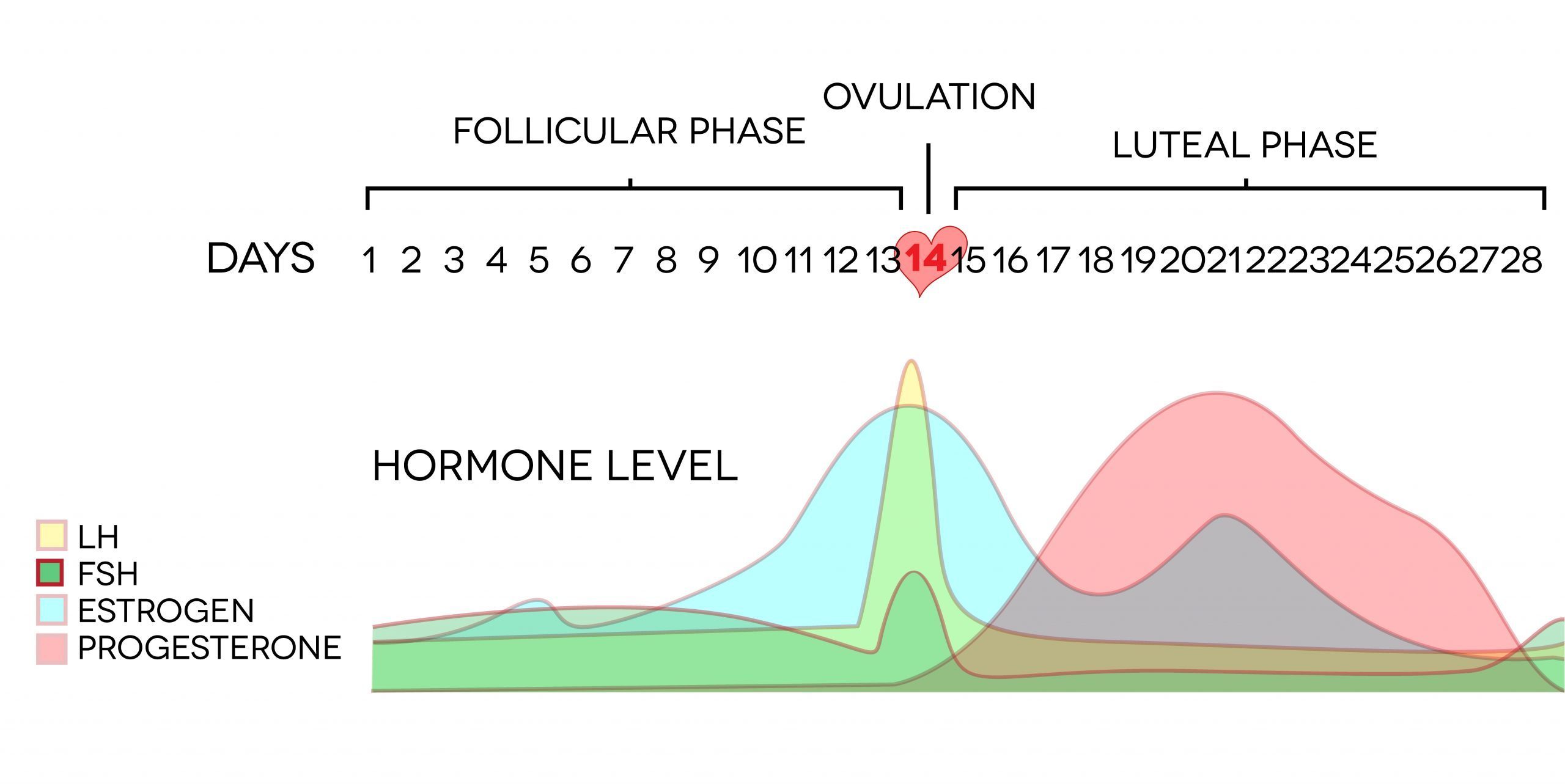
Understanding Luteal Phase Defect and its Symptoms
A luteal phase defect (LPD) occurs when the lining of your uterus doesn’t thicken enough to support a pregnancy after ovulation. This can lead to infertility or early pregnancy loss.
Recognizing the Signs
Identifying LPD isn’t always straightforward, as symptoms can be subtle or mimic other conditions. However, some common indicators include:
- Short luteal phase (less than 10 days): This is often diagnosed through charting your menstrual cycle.
- Spotting or light bleeding mid-cycle, between periods.
- Infertility: Difficulty conceiving after a year of trying (or six months if you’re over 35).
- Repeated miscarriages, especially early in pregnancy.
- Premenstrual symptoms (PMS) that are unusually severe or prolonged.
The severity of symptoms varies greatly between individuals. Some women experience only mild discomfort, while others suffer significantly. Accurate diagnosis requires medical evaluation.
Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
LPD arises from a hormonal imbalance affecting progesterone production after ovulation. Progesterone, crucial for preparing the uterine lining for implantation, may be insufficient. This deficiency can stem from various factors including:
- Ovulatory dysfunction: Problems with egg release.
- Underlying medical conditions: Thyroid problems, PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome).
- Stress: Chronic stress significantly impacts hormonal balance.
- Poor nutrition: Dietary deficiencies can affect hormone production.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment planning. They can conduct tests, such as blood work or endometrial biopsy, to confirm LPD and rule out other causes of infertility or pregnancy loss. Self-diagnosis is unreliable and can delay appropriate medical intervention.
How Prometrium Works to Correct Luteal Phase Deficiency
Prometrium, containing micronized progesterone, addresses luteal phase deficiency by supplementing the body’s natural progesterone production. This hormone plays a vital role in preparing the uterine lining for implantation. Insufficient progesterone levels hinder this process, leading to irregular cycles or infertility.
Mimicking the Natural Process
Prometrium works by mimicking the action of naturally produced progesterone. It thickens the uterine lining, creating a suitable environment for a fertilized egg to implant. This increased thickness provides a stable, nutrient-rich bed for the embryo to develop. Consistent progesterone levels, provided by Prometrium, promote regular menstrual cycles.
Specific Actions and Results
The medication directly influences endometrial receptivity. This means it improves the ability of the uterine lining to accept and support a fertilized egg. Successful implantation is more likely with sufficient progesterone. Further, it helps stabilize the uterine lining, reducing the chances of early pregnancy loss. Prometrium’s bioidentical nature ensures a natural physiological response, mimicking the body’s own hormone production. Regular use, as prescribed by a physician, can help to restore regular ovulation and menstruation.
Important Note
Always consult your doctor before starting Prometrium or any medication. They can assess your individual needs and determine the correct dosage and treatment duration. This information is for educational purposes and does not substitute professional medical advice.
Dosage and Administration of Prometrium for LPD
Prometrium, containing micronized progesterone, is typically administered vaginally. The recommended dosage varies depending on individual needs and response, but a common starting point is 200 mg at bedtime. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose based on your specific situation and may adjust it as needed.
Vaginal administration offers several advantages. It bypasses first-pass metabolism in the liver, leading to higher progesterone levels in the body compared to oral administration. This method also often results in fewer side effects.
Some women may experience slight irritation or spotting with vaginal use. If this occurs, discuss it with your physician. They can adjust your dose or explore alternative administration methods.
Consistent daily use is key. Adherence to the prescribed schedule is crucial for achieving optimal results. Remember to take Prometrium as directed by your doctor.
Oral administration is an alternative, but lower progesterone levels may result. Your physician will guide you on the best approach, weighing the benefits and potential drawbacks of each method. Close monitoring and regular follow-up appointments are recommended to assess treatment response and make any necessary adjustments to your Prometrium regimen.
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Prometrium
Prometrium, while often helpful, can cause side effects. These vary in severity and frequency. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, headache, and nausea. Less common, but still possible, are breast tenderness, mood changes, and changes in menstrual bleeding.
Serious Side Effects
While rare, serious side effects exist. These include allergic reactions (such as rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing), blood clots, and liver problems. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these.
Before starting Prometrium, discuss your medical history with your doctor. This includes any pre-existing conditions, current medications, and allergies. This helps assess potential risks and allows for informed decision-making. Regular check-ups during treatment are recommended to monitor your progress and address any emerging concerns.
Remember that this information is for general knowledge and shouldn’t replace advice from your healthcare provider. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance.
Prometrium vs. Other Treatments for Luteal Phase Defect
Progesterone supplementation, like Prometrium, is a common first-line treatment. However, other options exist, depending on the individual’s specific situation and the underlying cause of the luteal phase defect. Clomiphene citrate, for instance, stimulates ovulation and can sometimes improve luteal phase function indirectly. This medication is often considered if ovulation is irregular.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle adjustments, including stress reduction techniques (yoga, meditation), regular exercise, and a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, may also play a supportive role. These improvements can enhance overall reproductive health and potentially improve luteal phase length and function. These lifestyle changes should be considered alongside, not instead of, medical interventions if a luteal phase defect is diagnosed.
Alternative Therapies
Other options, such as acupuncture or herbal remedies, lack extensive scientific evidence supporting their efficacy in treating luteal phase defect. While some individuals report improvements, these treatments require further research before widespread recommendation. Always discuss alternative therapies with your healthcare provider before initiating them, especially if you are already undergoing medical treatment.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prometrium and LPD
Schedule a doctor’s appointment if Prometrium doesn’t alleviate your symptoms within a reasonable timeframe, typically a few cycles. This means you should contact your physician if you continue experiencing irregular periods, persistent heavy bleeding, or ongoing difficulties conceiving.
Prometrium Side Effects: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any serious side effects, such as severe headaches, chest pain, shortness of breath, or significant changes in mood or behavior. Also, report any allergic reactions like rash, itching, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. These warrant prompt medical evaluation.
Concerns About Dosage or Treatment Plan
Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns you have about your Prometrium dosage, the treatment plan’s progress, or potential interactions with other medications. Regular communication with your physician ensures optimal management of your LPD and ensures your safety and well-being.
Remember: Open communication with your doctor is key to successful treatment. Your healthcare provider can adjust your treatment plan as needed based on your individual response to Prometrium.