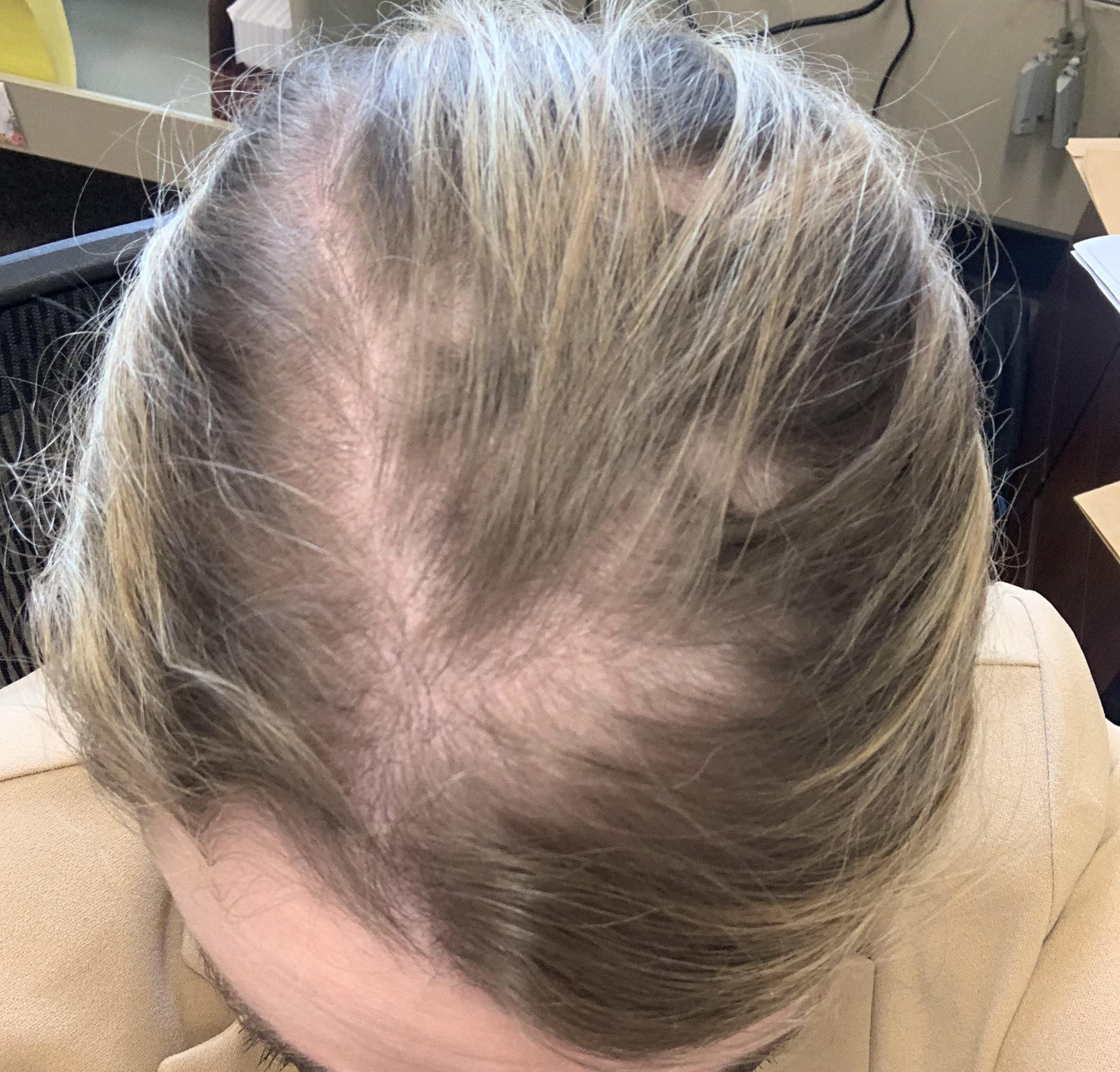
Experiencing hair thinning while on Accutane (isotretinoin) can be alarming, but knowing what to expect empowers you to take proactive steps. Accutane, a powerful medication for severe acne, sometimes disrupts the normal hair growth cycle, pushing a higher-than-usual percentage of hair follicles into the resting phase. This temporary imbalance, termed telogen effluvium, can lead to noticeable shedding.
The good news? Hair loss from Accutane is usually temporary. Studies indicate that hair regrowth typically begins within a few months after stopping the medication. To minimize shedding during treatment, prioritize a diet rich in protein and iron, which are building blocks for hair. Consuming at least 50 grams of protein daily, combined with iron-rich foods like spinach and lentils, can support hair follicle health. Consult your doctor about whether iron supplements are right for you, as excessive iron can also be detrimental.
Furthermore, handle your hair gently. Avoid tight hairstyles like ponytails or braids that can put stress on the hair follicles. When shampooing, use a mild, sulfate-free formula and avoid excessive heat styling. Minoxidil, an over-the-counter topical treatment, can sometimes help stimulate hair regrowth. Discuss its suitability with your dermatologist. If hair loss persists several months after discontinuing Accutane, consult your physician to rule out other potential causes such as thyroid issues or nutrient deficiencies.
- Accutane and Hair Loss: A Comprehensive Guide
- Managing Hair Thinning During Accutane Treatment
- Understanding Telogen Effluvium
- What to Expect After Accutane
- What is Accutane and How Does it Work?
- Who Should Consider Accutane?
- Important Considerations
- Does Accutane Cause Hair Loss? The Evidence.
- What the Research Says
- Managing Hair Loss During Accutane Treatment
- Temporary vs. Permanent Hair Loss: What to Expect
- Risk Factors: Who is More Likely to Experience Hair Loss?
- Pre-existing Hair Conditions
- Managing Hair Loss During Accutane Treatment
- Protect Your Hair
- Scalp Care Matters
- Post-Accutane: Regrowth and Recovery Strategies
- When to Consult a Doctor About Hair Loss
Accutane and Hair Loss: A Comprehensive Guide
If you experience hair thinning while taking Accutane, immediately contact your dermatologist to discuss potential dosage adjustments. Reducing your dosage may slow or stop the hair loss.
Understand the risk: Accutane, a powerful medication for severe acne, can unfortunately lead to hair thinning or, in rare instances, hair loss. This happens because Accutane reduces sebum production, which can affect the hair follicles.
Managing Hair Thinning During Accutane Treatment
- Consult your doctor: Discuss your concerns and explore options like lowering the dosage or adding supportive treatments.
- Use gentle hair products: Opt for sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners to minimize further damage.
- Avoid heat styling: Limit the use of hair dryers, curling irons, and straighteners. High heat can weaken hair.
- Eat a balanced diet: Ensure you’re consuming sufficient protein, iron, and vitamins to support hair health.
- Consider supplements: Your dermatologist might recommend supplements like biotin or collagen, but always consult with them first.
Understanding Telogen Effluvium
Accutane can trigger telogen effluvium, a temporary hair loss condition where a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting phase (telogen) prematurely. This typically results in noticeable shedding a few months after starting the medication.
What to Expect After Accutane
In most cases, hair growth returns to normal after you stop taking Accutane. The recovery process may take several months. Be patient and continue supporting your hair health during this time.
- Continue using gentle hair care practices.
- Maintain a healthy diet and consider supplements as advised by your doctor.
- Manage stress, as stress can contribute to hair loss.
If you’re concerned about persistent hair loss after completing your Accutane treatment, see a dermatologist. They can assess your hair and scalp and recommend suitable treatments, such as minoxidil or other therapies.
What is Accutane and How Does it Work?
Accutane, also known as isotretinoin, is a powerful oral medication doctors prescribe to treat severe, persistent acne that hasn’t responded to other treatments. It’s a retinoid, meaning it’s related to vitamin A.
Accutane works by targeting multiple factors that contribute to acne development. Here’s how:
- Reduces oil production: It dramatically shrinks the size of sebaceous glands, which produce oil. This leads to less oil on the skin, reducing the likelihood of clogged pores.
- Decreases inflammation: Accutane has anti-inflammatory properties, calming the redness and swelling associated with acne breakouts.
- Inhibits Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes): This bacterium contributes to acne. Accutane indirectly reduces its presence by creating an environment less conducive to its growth.
- Normalizes skin cell turnover: Accutane helps skin cells shed more effectively, preventing them from sticking together and clogging pores.
Who Should Consider Accutane?
Doctors usually reserve Accutane for individuals with severe cystic acne, nodular acne, or acne that is causing significant scarring and has not improved with other therapies such as topical treatments, antibiotics, or other acne medications.
Important Considerations
Due to its potential side effects, Accutane requires careful monitoring and strict adherence to prescribed guidelines. Pregnancy is strictly prohibited during Accutane treatment due to a high risk of severe birth defects. Patients must use two forms of effective contraception during treatment and for one month afterward. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor liver function, cholesterol levels, and other potential side effects.
Does Accutane Cause Hair Loss? The Evidence.
Accutane, also known as isotretinoin, *can* contribute to hair thinning or hair loss for some individuals. Studies suggest a potential link, although it’s not a guaranteed side effect for everyone. The exact mechanism isn’t fully understood, but the drug’s impact on sebum production is believed to play a role.
Isotretinoin significantly reduces sebum, an oily substance that keeps hair moisturized and healthy. This reduction can make hair brittle and prone to breakage. Some people report diffuse thinning, meaning hair loss all over the scalp, not just in patches.
What the Research Says
While larger studies directly linking Accutane and significant hair loss are limited, individual case reports and smaller trials have shown a correlation. A dermatologist might suggest monitoring your hair’s condition closely while on Accutane. Let them know if you notice increased shedding or changes in hair texture.
Managing Hair Loss During Accutane Treatment
If you experience hair thinning while taking Accutane, several strategies can help. Discuss using gentle shampoos and conditioners with your doctor or a dermatologist. Avoid harsh treatments like perms, relaxers, or excessive heat styling. Consider taking a daily multivitamin, particularly one containing biotin, as some believe this nutrient supports hair health. Ensure you’re getting adequate protein in your diet, as protein is essential for hair growth. Most importantly, consult your prescribing doctor before starting any new supplements. Finally, be aware that any hair loss related to Accutane is typically temporary and hair usually regrows after completing the treatment.
Temporary vs. Permanent Hair Loss: What to Expect
Expect hair loss from Accutane to be temporary in the vast majority of cases. Telogen effluvium, a temporary shedding phase triggered by medication, is the usual culprit. Your hair growth cycle should normalize a few months after you stop taking the medication. Monitor your shedding pattern. Noticeable thinning across your scalp suggests telogen effluvium.
However, while rare, permanent hair loss is theoretically possible, although direct causation from Accutane is often difficult to prove. Discuss persistent and significant hair loss with your doctor. Factors like genetics, underlying conditions, and other medications can play a role. Your doctor can assess if your hair follicles are damaged or shrinking, which can lead to permanent loss.
To promote hair regrowth during and after Accutane treatment, consider these strategies:
- Use a gentle, sulfate-free shampoo and conditioner.
- Avoid harsh styling practices like tight hairstyles and excessive heat.
- Consume a balanced diet rich in protein, iron, and vitamins.
- Discuss biotin supplements with your doctor. While generally safe, high doses may interfere with lab tests.
Consider consulting a dermatologist if you have prolonged hair loss. They can perform tests to rule out other causes and recommend specific treatments. The following table outlines potential steps and when to seek professional help:
| Symptom | Action | When to Seek a Dermatologist |
|---|---|---|
| Increased shedding within 1-3 months of starting Accutane | Continue gentle hair care practices; monitor progress. | If shedding persists beyond 6 months after stopping Accutane. |
| Noticeable thinning concentrated in specific areas | Rule out other causes with your primary care physician. | If thinning worsens or does not improve after addressing potential underlying issues. |
| Itchy or inflamed scalp | Address potential scalp conditions with a doctor. | Immediately. |
Risk Factors: Who is More Likely to Experience Hair Loss?
You’re more susceptible to hair thinning during Accutane treatment if you have a family history of hair loss (androgenetic alopecia). Genetics play a significant role in how your hair reacts to isotretinoin.
Higher Accutane dosages elevate the risk. Doctors typically aim for cumulative doses around 120-150 mg/kg over the course of treatment. Exceeding this range might place extra stress on hair follicles.
Pre-existing Hair Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing conditions like telogen effluvium or diffuse hair thinning may experience a noticeable acceleration of hair shedding while on Accutane. Consult a dermatologist beforehand to address these issues.
Nutritional deficiencies can worsen hair loss. Ensure you’re getting adequate iron, zinc, and biotin through diet or supplements (after consulting a doctor). Accutane can sometimes affect nutrient absorption.
Longer treatment durations increase the likelihood of hair changes. If your course extends beyond the typical 4-6 months, monitor your hair closely and discuss any concerns with your dermatologist. They might suggest adjusting the dosage or exploring supportive therapies.
Managing Hair Loss During Accutane Treatment
Combat hair thinning from Accutane by using gentle hair care products. Opt for sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners to minimize further damage. These mild formulations cleanse without stripping your hair of its natural oils, which is already a concern with Accutane’s drying effects.
Supplement your diet with biotin and collagen. These nutrients can potentially support hair follicle health and promote stronger hair growth. Consult with your doctor to determine the appropriate dosage for you. Adding foods rich in these nutrients, like eggs and leafy greens, can also be beneficial.
Protect Your Hair
Avoid harsh styling practices like frequent heat styling with blow dryers, straighteners, and curling irons. The high heat weakens the hair shaft and makes breakage more likely. Instead, allow your hair to air dry whenever possible, and use heat protectant sprays if you must use heat styling tools. Also, be gentle when brushing. Use a wide-tooth comb and gently detangle from the ends, working your way up to the roots.
Scalp Care Matters
Improve scalp circulation with regular scalp massages. Use your fingertips to gently massage your scalp for a few minutes each day. This can stimulate blood flow to the hair follicles, which may help to encourage hair growth. Consider using a lightweight carrier oil, like coconut or jojoba oil, to nourish the scalp during the massage. Monitor changes and consult your dermatologist if concerns persist.
Post-Accutane: Regrowth and Recovery Strategies
Stimulate your scalp with gentle massage techniques. Use your fingertips to apply circular motions for five to ten minutes daily. This encourages blood flow and nourishes hair follicles, promoting growth.
Choose hair products with ingredients known to support hair health. Look for shampoos and conditioners that contain biotin, keratin, or saw palmetto. These components help strengthen strands and reduce breakage. Avoid harsh sulfates and excessive heat styling, which can weaken hair.
Consider incorporating supplements into your diet. Omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and iron can play a role in hair growth. Discuss supplementation with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage for your individual needs. A balanced diet is critical, prioritizing protein-rich foods like eggs, lean meats, and legumes.
Manage stress levels through relaxation practices. Chronic stress can contribute to hair thinning. Explore activities like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature to promote well-being and potentially improve hair health. Adequate sleep also impacts hormone levels, thereby affecting the hair growth cycle. Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night.
If hair loss persists beyond several months after discontinuing Accutane, consult a dermatologist. They can evaluate your scalp and hair, rule out other potential causes, and recommend targeted treatments, such as minoxidil, or other interventions suited to your specific situation. Early intervention often yields better outcomes.
Protect your hair from environmental damage. Wear a hat or scarf when exposed to strong sunlight or cold temperatures. This helps minimize dryness and breakage. Regular trims are also beneficial, removing split ends and preventing further damage up the hair shaft.
Be patient and consistent with your hair care regimen. Regrowth takes time, and visible improvements may not occur immediately. Track your progress by taking photos every few weeks to monitor changes. Celebrate small victories along the way.
When to Consult a Doctor About Hair Loss
See a doctor immediately if your hair loss is sudden, patchy, and accompanied by scalp pain, itching, or redness. Rapid hair loss can signal an underlying medical condition requiring prompt attention.
Schedule a consultation if you notice a drastic change in the texture or thickness of your hair. Thinning that occurs over a short period (weeks or months) is more concerning than gradual thinning over several years. Consider tracking hair shedding rate to understand the severity of the problem.
If you’re experiencing hair loss alongside other symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, or skin problems, consult a physician. These could indicate a systemic illness like thyroid disease or lupus contributing to the hair thinning.
Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if hair loss is significantly impacting your emotional well-being. Doctors can offer solutions and connect you with support services to manage the psychological effects of hair thinning.
Consult a doctor if you’re considering treatments like Accutane and hair loss becomes excessive. Discussing potential side effects and preventive strategies before treatment starts can help minimize potential hair-related issues. A dermatologist can evaluate your specific risk factors and customize a treatment plan.
Consider a doctor’s visit if you have a family history of early hair loss. Genetic predisposition can make you more susceptible to certain hair loss conditions, and a medical evaluation can help identify potential preventative measures.